Arutelu:Läti
Siin on inglisekeelsest vikipeediast võetud tekst, mis on osaliselt eesti keelde tõlgitud. Me ei pea teksti üks-ühele üle võtma. Pildid tuleb eesti vikipeediasse üles laadida.
Teen ettepaneku kasutada eeskujuna artiklit Albaania. Tolle artikli bäotel võib ka üldist formaati arutada. Andres 00:06, 21 Dec 2003 (UTC)
| |||||
| National motto: None | |||||
 | |||||
| ametik keel | läti keel | ||||
| pealinn | Riia | ||||
| president | Vaira Vīķe-Freiberga | ||||
| peaminister | Einars Repše | ||||
| Area - Total - % water | Ranked 121st 64,589 km² 1.5% | ||||
| Population - Total (2001) - Density | Ranked 137th 2,385,231 37/km² | ||||
| iseseisvus - kuulutatud - tunnustatud | Venemaast 18. novembril, 1918 11. augustil, 1920 | ||||
| valuuta | latt | ||||
| ajavöönd | Ida-Euroopa aeg | ||||
| hümn | Dievs, Sveti Latviju | ||||
| üladomeen | .lv | ||||
| maakood (telefon) | 371 | ||||
History
Main article: History of Latvia
Known for the most part as Livonia, the area that now constitues Latvia was under the influence of the German Sword Brethren from the 13th century onward. However, in the 18th and 19th century, Russia gained control over Latvia and neighbouring regions. With Russia devastated by revolution and World War I, Latvia declared its independence in November 1918. This period of independence lasted only briefly, as the Soviet Union annexed the country in June 17, 1940 in accordance with the Soviet-Nazi agreement (Ribbentrop-Molotov pact) of 1939.
Except for a brief period of German occupation during World War II, Latvia remained Soviet territory until reforms in Soviet communism such as glasnost stimulated the Latvian independence movement, and Latvia regained its independence on August 21, 1991. It has since followed a course to reinforce its links with the West, and is slated to become a member of both NATO and the European Union in 2004.
Politics
Main article: Politics of Latvia
The 100-seat unicameral Latvian parliament, the Saeima, is elected by direct, popular vote every four years. The presidential elections are held separately, also every four years. The president is elected by Saeima. The president appoints a prime minister, who together with his cabinet, forms the executive branch of the government.
Haldusjaotus. Regioonid
Main article: Counties of Latvia
Latvia is divided into 26 counties called rajons. 7 cities have a separate status.
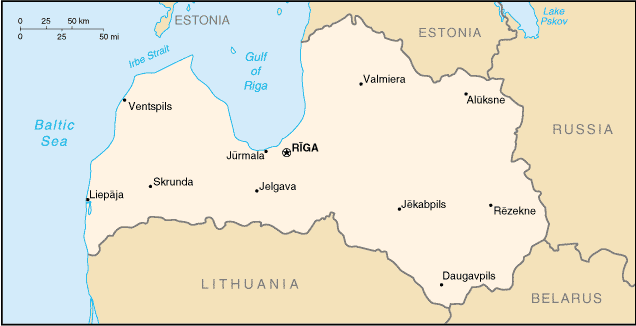
Geograafia
Suur osa Lätist on kaetud metsadega. Riigis on üle 12.000 valdavalt väikese jõe ja rohkem kui 3.000 järve. Enamus maast on madalik, kõrgeim tipp - Gaiziņkalns - ulatub vaid 312 m üle merepinna.
An inlet of the Baltic Sea, the shallow Liivi laht is situated in the northwest of the country. The capital city Riga is located on the shores of this inlet, where the Daugava river flows into it. Other major cities include Daugavpils further upriver and Liepaja along the Baltic coast.
The Latvian climate is maritime and temperate in nature, with cool summers and wet, moderate winters.
Majandus
Rahvastik
Kultuur
Lingid
- Läti valitsus - ame
- Presidendid kantselei - Official presidential site
- Saeima - parlamendi lehekülg
- Welcome to Latvia - Wide collection of Latvian links
- LatviansOnline - Popular online Latvian community
- latvians.com - Latvian identity in exile
Austria | Belgium | Denmark | Finland | France | Germany | Greece | Ireland
Italy | Luxembourg | Netherlands | Portugal | Spain | Sweden | United Kingdom
Countries acceding to membership on May 1, 2004:
Cyprus | Czech Republic | Estonia | Hungary | Latvia | Lithuania | Malta | Poland | Slovakia | Slovenia